Wireless charging has become a defining feature of modern smartphones, reshaping how users power their devices at home, in offices, and on the move. While many consumers enjoy the convenience of cable-free charging, fewer truly understand how the technology works behind the scenes.
For smartphone brands, product managers, and buyers, understanding juhtmevaba laadimine technology is more than a technical curiosity. It directly impacts product design, charging performance, safety, cost control, and user experience. In this article, we explain how wireless charging works in modern smartphones, why it has become reliable at scale, and what brands should consider when adopting it.
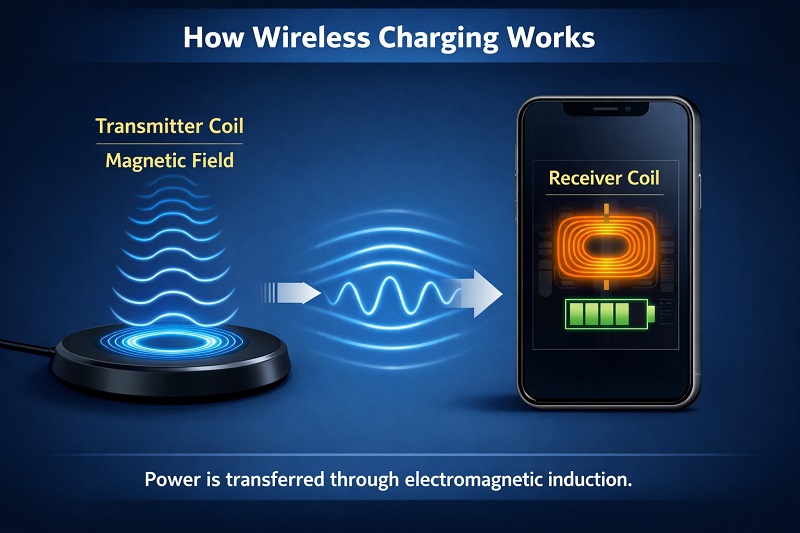
The Basic Principle Behind Wireless Charging
At its core, wireless charging is based on electromagnetic induction. Instead of transferring electricity through a physical cable, energy is transmitted wirelessly between two coils.
One coil is located inside the wireless charger, known as the transmitter coil. The other is built into the smartphone, known as the receiver coil. When the charger is connected to a power source, it generates an alternating electromagnetic field through the transmitter coil. When a smartphone is placed on the charging surface, the receiver coil captures this energy and converts it back into electrical current to charge the battery.
This process happens automatically and invisibly, creating a seamless charging experience for the user.
The Role of Qi Wireless Charging Standards
Most modern smartphones rely on the Qi wireless charging standard, which is widely adopted across the global consumer electronics industry. Qi defines how wireless power transfer should work, including power levels, communication protocols, and safety requirements.
By following a unified standard, smartphone brands ensure compatibility with a wide range of third-party wireless chargers. This reduces user friction and allows brands to confidently integrate wireless charging into their devices without locking customers into proprietary accessories.
From a manufacturing and sourcing perspective, Qi certification also simplifies product development and compliance testing, especially for brands targeting international markets.
Communication Between Charger and Smartphone
Wireless charging is not just about transferring power. Modern systems involve continuous communication between the charger and the smartphone.
Once a device is placed on a wireless charger, the two components exchange data to determine optimal charging conditions. This includes identifying the device, confirming power requirements, monitoring temperature, and adjusting output in real time.
If a foreign object, such as a metal key or coin, is detected between the phone and the charger, the system can reduce or stop power transmission to prevent overheating or safety risks. This intelligent communication is a key reason why wireless charging today is far safer and more reliable than early-generation solutions.
How Power Levels Have Improved Over Time
Early wireless chargers typically delivered low power output, resulting in slow charging speeds. This limited adoption and created the perception that wireless charging was only suitable for overnight use.
Modern wireless charging technology has evolved significantly. Advances in coil design, power management chips, and thermal control now allow higher power transfer with improved efficiency. Fast wireless charging has become widely available, making wireless solutions practical for daily use rather than just convenience charging.
For smartphone brands, this improvement means wireless charging can now be positioned as a core feature rather than a secondary option.
Coil Design and Alignment Challenges
One of the technical challenges in wireless charging is coil alignment. For efficient power transfer, the transmitter and receiver coils must be properly aligned. Poor alignment can lead to energy loss, slower charging, or heat buildup.
To address this, manufacturers use optimized coil shapes, multi-coil layouts, and intelligent positioning systems. Some wireless chargers are designed with wider charging zones to improve user experience, while smartphones integrate precisely placed receiver coils to ensure stable performance.
From a product development standpoint, coil design plays a critical role in balancing charging speed, thermal performance, device thickness, and production cost.
Thermal Management and Safety Considerations
Heat management is one of the most important aspects of wireless charging technology. Because power is transferred through electromagnetic fields, some energy loss is inevitable, and this loss manifests as heat.
Modern wireless charging systems use multiple layers of protection to manage temperature. These include real-time temperature monitoring, intelligent power adjustment, and automatic shutdown when abnormal conditions are detected.
For smartphone brands, proper thermal design is essential not only for user safety but also for battery health and long-term device reliability. Well-engineered wireless charging solutions help extend battery lifespan and reduce performance degradation over time.
Integration Inside Modern Smartphones
Integrating wireless charging into a smartphone requires careful coordination between hardware and software. The receiver coil must be positioned precisely within the device while leaving room for the battery, camera modules, antennas, and other components.
In addition, materials used in the phone’s back cover affect wireless charging efficiency. Glass and certain composite materials allow electromagnetic fields to pass through more effectively than metal, which is why many wireless-charging-enabled smartphones feature glass backs.
This integration process highlights why close collaboration between smartphone brands and experienced manufacturing partners is crucial during development.
Wireless Charging Accessories and User Scenarios
Wireless charging is no longer limited to flat charging pads. Modern accessories include vertical charging stands, car-mounted wireless chargers, and multi-device charging stations.
These accessories support a wide range of user scenarios, such as video calls while charging, desk use in offices, or hands-free navigation in vehicles. For brands, offering compatible wireless charging accessories enhances the overall ecosystem and strengthens customer engagement.
From a technical standpoint, accessory design must account for device stability, viewing angles, airflow, and power consistency across different usage conditions.
Efficiency vs. Convenience: A Practical Balance
While wired charging remains slightly more efficient in pure energy transfer, wireless charging offers unmatched convenience. For most users, the ability to charge effortlessly throughout the day outweighs small differences in efficiency.
Modern wireless charging technology has narrowed this gap significantly. As efficiency improves and heat generation decreases, wireless charging continues to gain acceptance as a primary charging method rather than a secondary one.
For smartphone brands, understanding this balance helps position wireless charging accurately in product messaging and feature prioritization.
Why Understanding Wireless Charging Matters for Brands
For buyers, product managers, and engineers, understanding how wireless charging works enables better decision-making. It affects component selection, cost control, quality assurance, and long-term product strategy.
As wireless charging becomes a standard feature across more price segments, brands that fully understand the technology are better equipped to differentiate their products, optimize performance, and collaborate effectively with manufacturing partners.
This knowledge also supports faster development cycles and smoother transitions from concept to mass production.
Kokkuvõte
Wireless charging technology for modern smartphones is built on a combination of electromagnetic principles, intelligent communication, advanced thermal management, and precise engineering. What appears simple to the user is the result of years of technological refinement and industry collaboration.
As charging speeds improve and global standards continue to mature, wireless charging is becoming an essential part of smartphone design rather than an optional feature. For brands and buyers alike, understanding how this technology works is the first step toward leveraging its full potential in future products










